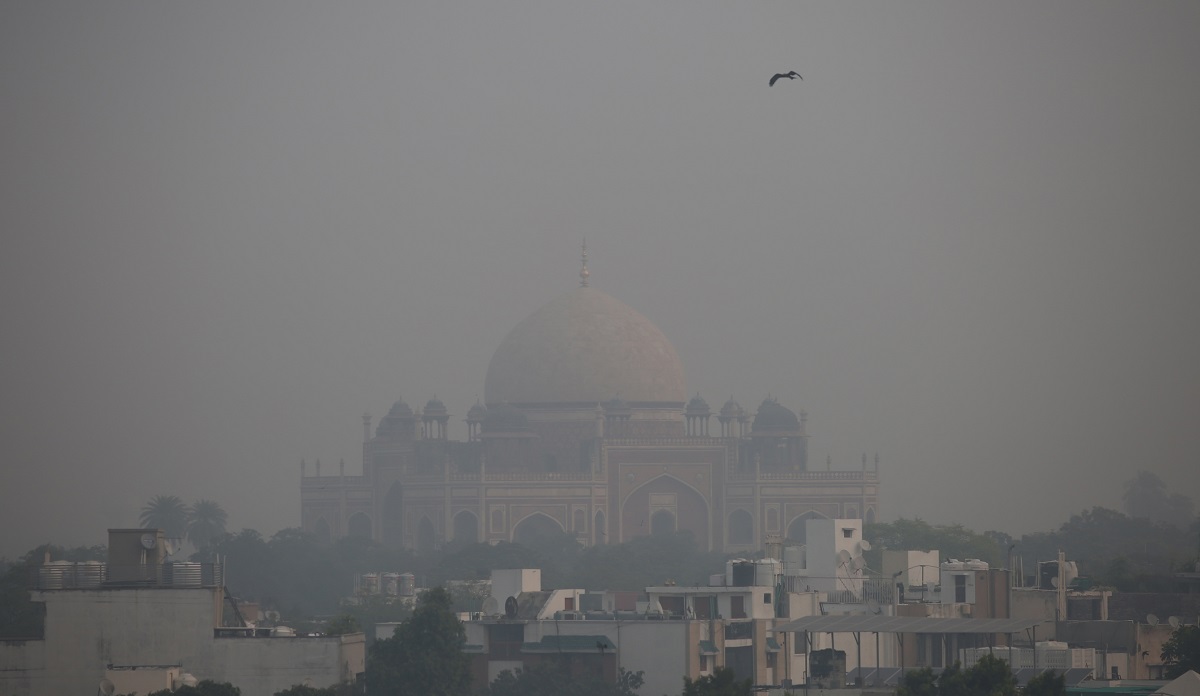
Air Quality Index (AQI) in Delhi NCR: A Comprehensive Analysis
The Air Quality Index (AQI) holds immense importance as a crucial gauge of the air quality within a specific area, serving as a vital tool in both public health and environmental management. The severe air pollution problems faced by Delhi and the surrounding National Capital Region (NCR) have recently brought considerable focus to the AQI. This extensive blog post aims to thoroughly explore the AQI in Delhi NCR, analyzing the various factors that contribute to the deterioration of air quality, its detrimental effects on health, and the proactive measures implemented to tackle this urgent issue.
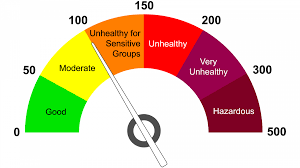
The Air Quality Index: What is it?
The Air Quality Index (AQI) is a globally standardized system for communicating the air quality in a specific area. It considers different pollutants, such as particulate matter (PM2.5 and PM10), ground-level ozone (O3), sulfur dioxide (SO2), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), and carbon monoxide (CO). The AQI provides a numerical value to represent the air quality, where lower values indicate better air quality and higher values indicate poorer air quality.
Factors Contributing to Poor Air Quality in Delhi NCR
Delhi NCR faces a complex set of challenges when it comes to air quality, many of which contribute to elevated AQI levels. Here are some key factors:
- Vehicular emissions: have significantly increased in Delhi due to the exponential growth in the number of vehicles on the city’s roads. This has resulted in the release of particulate matter and greenhouse gases into the atmosphere.
- Industrial activities in and around Delhi are also major contributors to air pollution. Emissions from factories, power plants, and construction activities release pollutants into the air, further deteriorating the air quality.
- Agricultural practices in the neighboring states of Punjab and Haryana, such as stubble burning during the post-harvest season, add to the pollution load in Delhi NCR.
- Weather Conditions: The region’s geographical location and weather patterns can exacerbate the problem of air pollution. Atmospheric stagnation caused by these factors can trap pollutants close to the ground, leading to poor air quality.
- Construction and Dust: Rapid urbanization and construction in Delhi contribute to high levels of dust and particulate matter in the air. This is a result of the increased construction activities and the generation of dust particles from these processes.
- Household Pollution: In some households, the use of solid fuels for cooking and heating adds to indoor air pollution. This household pollution further contributes to the overall air pollution in Delhi.

Health Impacts of Poor Air Quality Index
The high AQI levels in Delhi NCR have serious health consequences. Prolonged exposure to polluted air can lead to a range of health problems, including:
- Respiratory Issues: Air pollution can exacerbate respiratory conditions like asthma and bronchitis, and it can lead to the development of new respiratory problems.
- Cardiovascular Problems: Poor air quality is associated with an increased risk of heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular diseases.
- Reduced Lung Function: Children exposed to high levels of air pollution may experience reduced lung development, leading to long-term health effects.
- Premature Death: Severe air pollution is responsible for premature deaths and reduced life expectancy.
- Mental Health: Some studies suggest a link between air pollution and mental health issues, including depression and cognitive decline.
Government Initiatives and Measures to Improve Air Quality Index
Recognizing the severity of the air pollution problem, the government and various organizations have taken a range of measures to address it:
- Odd-Even Scheme: The Delhi government has implemented the odd-even scheme, which restricts the use of private vehicles on alternate days, reducing vehicular emissions.
- Supreme Court Directives: The Supreme Court has passed several directives to combat air pollution, including banning the sale of firecrackers during Diwali and regulating construction activities.
- NGT Regulations: The National Green Tribunal (NGT) has played a significant role in monitoring and enforcing environmental norms.
- Promotion of Electric Vehicles: Encouraging the use of electric vehicles can reduce air pollution from combustion engines.
- Air Quality Monitoring: Enhanced air quality monitoring systems have been put in place to provide real-time data to the public.
- Stubble Management: Efforts are being made to promote sustainable stubble management practices in neighboring states.

Individual Efforts for Cleaner Air Quality
While government initiatives are crucial, individual efforts also play a significant role in improving air quality:
- Reducing Vehicle Use: Carpooling, using public transportation, and adopting cycling or walking as modes of commuting can reduce vehicular emissions.
- Green Initiatives: Planting trees and supporting green initiatives can help improve air quality.
- Reducing Indoor Pollution: Using cleaner cooking fuels and improving indoor ventilation can reduce exposure to indoor pollutants.
- Air Purifiers and Masks: In highly polluted areas, using air purifiers and masks can offer some protection.
The Way Forward
Addressing the air quality crisis in Delhi NCR requires a multi-pronged approach involving government action, public awareness, and individual responsibility. Efforts to reduce emissions from vehicles, industries, and agriculture must be sustained and supported by strict enforcement of regulations. Additionally, investments in clean energy sources and sustainable urban planning are essential for long-term improvement.
In conclusion, the air quality in Delhi NCR, as reflected by the AQI, is a matter of grave concern. It impacts the health and well-being of millions of residents. While there have been significant efforts to address this issue, continued vigilance and comprehensive strategies are necessary to ensure that the region’s air quality becomes safer and healthier for all.
